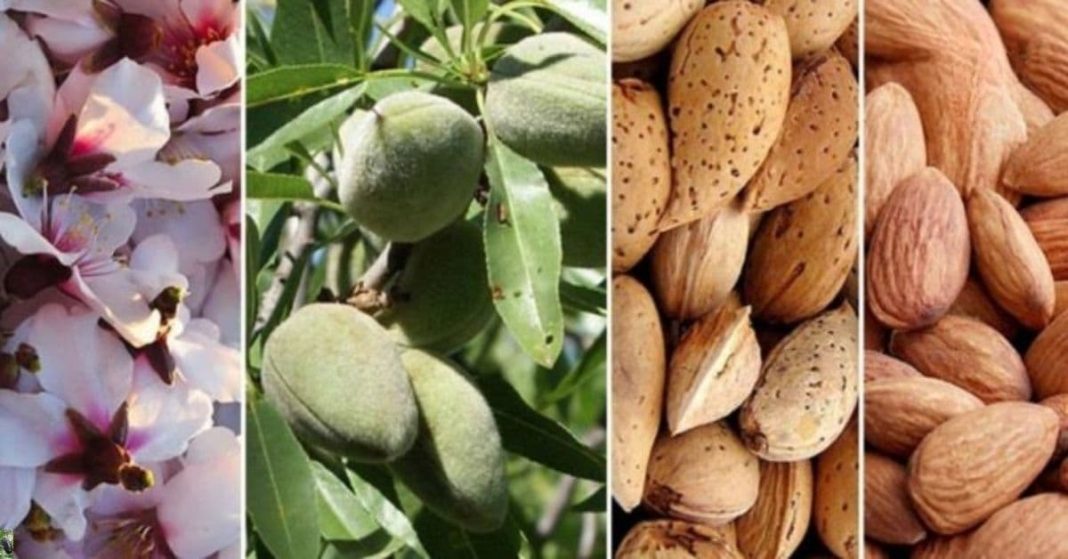
Almonds are among the most ancient and widely cherished nuts in the world, appreciated not only for their unique taste but also for their extraordinary health benefits. Although almonds are high in fat, scientific studies and centuries of tradition highlight them as one of the best foods you can add to your diet—especially for maintaining cardiovascular health.
At first glance, the idea may sound contradictory. People often assume that high-fat foods are harmful to the heart, but almonds are a striking exception. The key lies in the type of fat they contain. Rather than harmful saturated fats, almonds are rich in monounsaturated fatty acids, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that make them a powerful ally in protecting your heart, blood vessels, and overall well-being.
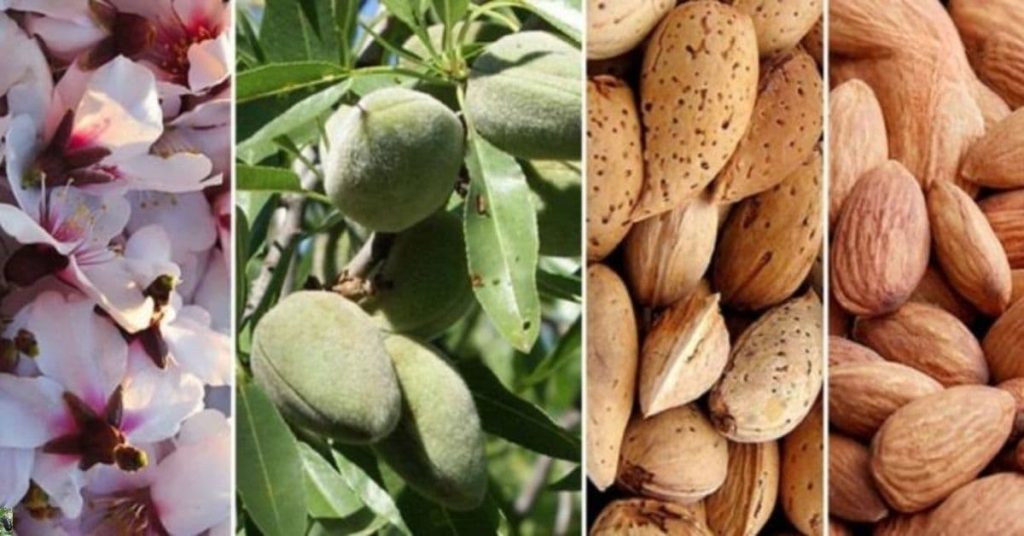

A Nut With Tradition and Symbolism
Almonds are not just a food; they are also a symbol of health and prosperity. In many countries, almonds are traditionally distributed during weddings. This custom dates back to Italy in 1350. Typically, guests are given five sugared almonds, each representing a blessing: health, happiness, wealth, fertility, and longevity.
This tradition, carried forward for centuries, reflects the deep cultural recognition of almonds as a food linked to vitality and good fortune. Today, modern science confirms what tradition long suggested: almonds truly do bring health benefits that extend beyond simple nutrition.
Nutritional Profile of Almonds
A single handful of almonds—approximately 30 grams—contains almost half its weight in oil. At first, this high-fat content might sound concerning. However, the majority of this fat is in the form of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs). These fats are scientifically proven to protect the cardiovascular system by reducing bad cholesterol (LDL) while maintaining or even increasing good cholesterol (HDL).
In addition, almonds provide:
- Vitamin E – a powerful antioxidant that prevents plaque buildup in arteries and reduces the risk of heart attack.
- Magnesium – essential for heart rhythm regulation and muscle function.
- Fiber – supporting digestion and cholesterol balance.
- Protein – helping maintain lean body mass and reducing hunger.
Eating just one handful of almonds daily can satisfy nearly half of your daily Vitamin E requirements, making them a nutritional powerhouse.
Almonds and Cardiovascular Health
A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition placed almonds on the list of heart-friendly foods. Research demonstrated that eating almonds regularly could significantly reduce bad cholesterol (LDL), which is one of the leading contributors to cardiovascular disease.
In fact, almonds were shown to act similarly to cholesterol-lowering medications, offering a natural alternative for those who want to support heart health through diet. By reducing cholesterol levels, preventing arterial plaque buildup, and improving blood circulation, almonds directly contribute to lowering the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Almonds and Obesity
Obesity is one of the major risk factors for cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and metabolic disorders. It often develops due to poor dietary habits, lack of exercise, chronic stress, overeating, and insufficient sleep.
Here too, almonds can play a supportive role. Despite their high fat content, they are remarkably effective in weight management. Why? Because the fats in almonds are absorbed slowly and provide long-lasting satiety. Eating a handful of almonds can help you feel full, reducing cravings for sugary or refined carbohydrate foods.
A study conducted by King’s College London confirmed that almonds reduce carbohydrate absorption and encourage the body to burn its own fat reserves. Both men and women experienced increased satiety and improved metabolic responses when consuming almonds compared to other snack foods.
For maximum benefit, experts recommend eating one handful of raw (unroasted) almonds daily. Roasted almonds, especially those fried in oil or salted, lose some of their nutritional quality and can contribute to excess calorie intake.
Almonds and Alzheimer’s Disease
Beyond cardiovascular health and weight control, almonds also have a role in brain health. Research has suggested that almonds may help reduce the risk of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease.
In one study, laboratory animals predisposed to Alzheimer’s were divided into two groups. One group was fed a diet enriched with almonds, while the other group consumed a regular diet. After four months, the almond-fed group performed significantly better on memory tests.
This finding is particularly encouraging for middle-aged and older adults. Scientists now recommend incorporating a daily handful of raw almonds as part of a preventive strategy for cognitive health.
Almonds and Colon Cancer Prevention
The health benefits of almonds extend even further. A study conducted at the University of California, Davis investigated the potential of almonds in protecting against colon cancer. The results were promising: almonds reduced certain biomarkers associated with colon cancer risk.
This protective effect is likely due to the high levels of fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats in almonds, all of which work together to support gut health, regulate digestion, and protect cells from oxidative damage.
Practical Tips for Eating Almonds
- Choose raw almonds over roasted or salted varieties.
- Avoid almond-coated candies (like sugared almonds at weddings) for daily consumption—they contain excess sugar.
- Soak almonds overnight to improve digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Blend almonds into smoothies, sprinkle them over salads, or enjoy them as a snack between meals.
- Stick to the recommended portion: about one handful (30 grams) per day.
Doctor’s Perspective
Medical experts increasingly agree that almonds are more than just a snack. They are a functional food—a natural medicine that supports multiple body systems.
- For the heart, they reduce LDL cholesterol, lower blood pressure, and improve vascular function.
- For weight management, they provide satiety and prevent overeating.
- For the brain, they enhance memory and may reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s.
- For the digestive system, they improve gut microbiota and reduce colon cancer risk.
However, moderation is essential. Almonds are calorie-dense, and overconsumption may lead to excess calorie intake. For most adults, 30 grams daily is the ideal amount.
Conclusion
Almonds are not only delicious but also an incredibly powerful food for overall health. Despite being high in fat, their unique nutrient composition—monounsaturated fats, Vitamin E, antioxidants, and minerals—makes them a vital part of a heart-healthy diet.
From protecting cardiovascular health and helping with weight management, to supporting brain function and even reducing cancer risks, almonds truly earn their reputation as a superfood.
So the next time you’re looking for a nutritious snack, skip the chips or sweets and reach for a handful of almonds. With consistent consumption, you are not only nourishing your body but also protecting your future health.
Vau.ge – Your Daily Guide for Practical Advice!
Vau.ge is a place where caring for your health, beauty, and daily routines becomes a natural, accessible, and enjoyable experience. Our main goal is to provide you with reliable information about natural remedies, homemade recipes, and practical tips that help you live a healthier life, look better, and simplify your everyday tasks without unnecessary expenses.
Our tips are easy to incorporate into your everyday life — whether it’s skincare, haircare, health-boosting remedies, or small tricks to save time. This knowledge will not only improve your own life but also allow you to share the experience with others, giving more people the chance to live a balanced life naturally and economically.
Please note: The articles on our website are for informational purposes only and do not replace professional medical advice. If you have serious health concerns, please consult a qualified specialist.