A heart attack is one of the most common health issues worldwide. It can occur in both men and women. The survival rate is high, which means that if you recognize the warning signs early, it is possible to recover and resume a normal life after this traumatic event. Therefore, everyone should be aware of the symptoms and warning signs of a heart attack so that they can take the necessary steps in emergency situations.
Symptoms of a Heart Attack – Warning Signs:
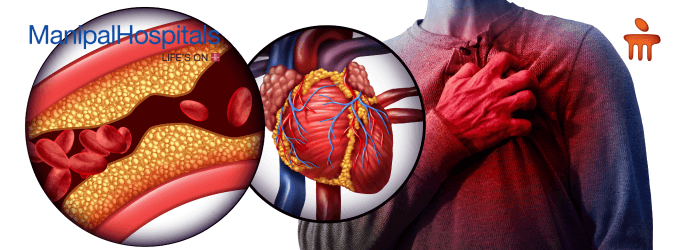
Chest Pain and Discomfort:
- One of the most common symptoms associated with a heart attack is severe chest pain and the sensation of pressure. This pain may radiate not only in the chest area but also to the arms, neck, jaw, or back. Most commonly, the pain appears on the left side, but it can occur on both sides of the chest.
- The pain typically lasts for several minutes but can often recur. This can sometimes be mistaken for indigestion or heartburn.
- The location of the pain is usually in the center of the chest, but it can also occur in the arms and neck. If there are other symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, or increased heart rate, these can indicate the possibility of a heart attack.
- Especially in women, chest pain might not always be obvious or clear, which makes the additional symptoms even more important.
Shortness of Breath:
- People suffering from a heart attack may have difficulty breathing. This is caused by the pressure and tightness in the chest, which affects the lungs.
- Shortness of breath can happen even at rest and is typically aggravated by physical activity.
- It may become more noticeable when the person tries to engage in any form of physical activity or even during simple rest.
Dizziness:
- People experiencing a heart attack often report feeling dizzy or light-headed. This is a direct indication of compromised blood flow to the heart and brain.
- This sensation can also feel like weakness or a fainting-like experience, further confirming a potential heart issue.
Cold Sweats:
Individuals with a heart attack often experience cold sweats. This is due to the body’s stress response, which can result in feelings of shock or anxiety.
Cold sweats are a very distinct symptom, and anyone experiencing them should be alert to the possibility of a heart attack.
Other Common Symptoms of a Heart Attack:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Sudden fatigue, which might occur even without physical exertion.
- Anxiety, feelings of panic, and sometimes headaches.
People often don’t realize the symptoms of a heart attack until an emergency happens.
Risk Factors:
Age Factor:
- Age is a primary risk factor. Men over the age of 45 and women over the age of 55 are at increased risk. People in these age groups should take all necessary precautions to prevent a heart attack.
High Blood Pressure:
- High blood pressure is one of the most common risk factors for heart attacks. When blood pressure rises, it causes blood to flow more forcefully through the arteries, which can damage them and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- High blood pressure can significantly increase the chances of a heart attack because it creates excessive strain on the heart.
High Cholesterol:
- Cholesterol comes in different types: triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL and VLDL are known as “bad” cholesterol, which can accumulate in the arteries and cause plaque buildup.
- High levels of LDL and VLDL can increase the risk of a heart attack. On the other hand, HDL is considered “good” cholesterol because it helps remove harmful cholesterol from the bloodstream.
Diabetes:
- Diabetes means the body has trouble managing sugar levels. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels, making it more difficult for the heart to get adequate oxygen.
- This can increase the risk of a heart attack as the body becomes resistant to insulin or produces insufficient amounts of it.
Genetic Factors:
- People are at higher risk if their siblings, parents, or grandparents had heart attacks at an early age (before 45 for men and 65 for women).
- Genetics play an essential role in determining whether an individual is more likely to experience heart disease or a heart attack.
Obesity:
- Obesity is a significant contributing factor to heart disease. Weight gain often leads to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes, all of which are factors that increase the risk of heart attacks.
- Even losing 10% of body weight can significantly improve overall health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
By understanding the key warning signs of a heart attack and identifying risk factors, you can be better prepared to act quickly and potentially save a life. Recognizing these symptoms early can make all the difference in a successful recovery.


















